In the vast world of the internet, where information abounds, the presence of search engines is paramount. They serve as the index to navigate this vast digital library. Among the plethora of search engines, none shines brighter than Google. Let’s embark on a journey to uncover the colossal entity that is the Google Search Engine.

Beginnings of Google
In 1996, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, two Stanford Ph.D. students, began working on a search algorithm called “Backrub.” By 1997, this began to develop into what we now call Google, a play on the mathematical term ‘googol’, which indicates a number followed by a hundred zeros. The name represents the company’s goals to organize the internet’s seemingly unlimited amount of information.
How Does Google Work?
Google operates primarily through three processes:
Crawling: This is the phase of discovery in which ‘Googlebots’ scan the internet for new and updated content. These bots begin with a list of URLs from previous crawls and then branch out to sitemap data provided by website owners.

Indexing: Once a page is found, Google examines what is on it, such as natural text, and drives it in the Google Index, a massive database stored on hundreds of computers.
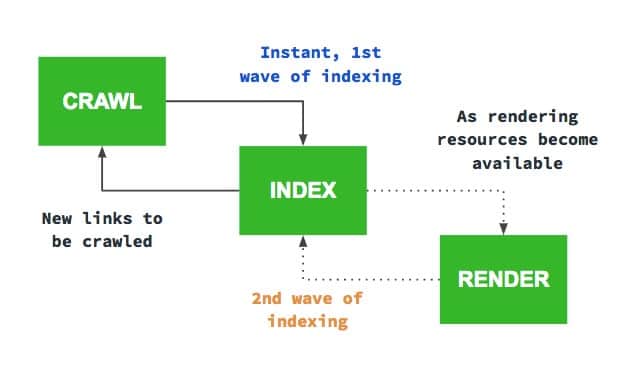
Ranking: When a search query is entered, Google searches the index and delivers results that are relevant and useful to the searcher’s query, ranking them based on a variety of factors such as relevance and website quality.
Algorithms: The Vibrant Center of Digital Exploration
Google’s search algorithms are a closely guarded secret. However, it’s known that they analyze numerous factors, including:
Keywords: The actual words users type into the search box.
Relevance: Matching content to query intent.
Quality of content: Well-researched, regularly updated content often ranks higher.
Usability of webpages: Mobile-friendliness, site speed, and so on.
Context and settings: Search history, location, and settings play a part in tailoring the results.
Over the years, Google has rolled out several major algorithm updates such as Penguin, Panda, and BERT to better understand user queries and webpage content.
SEO
Webmasters use Search Engine Optimization (SEO) to rank better on Google’s Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs). It involves enhancing several components of a website, including content quality, meta tags, URL structure, and backlinks. Google’s technologies, such as Google Analytics and Search Console, can help webmasters with this.

Future of Google Search
Voice searches and visual searches (through Google Lens) are becoming more popular as Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence progress. Google’s BERT update (2019) demonstrates the company’s focus on Natural Language Processing (NLP) for enhanced context understanding.
Privacy Concerns and Google
There’s no denying the convenience Google offers. However, this has raised concerns regarding user privacy and data handling. Google’s move towards more personalized search results involves collecting and analyzing massive amounts of user data. Although Google claims to prioritize user privacy, it’s always recommended for users to periodically review their privacy settings.
Conclusion: The Google Search Engine, which changed the digital environment, is always evolving to keep up with technology breakthroughs and user habits. Understanding how technology works helps users not just use it to its maximum capacity, but also navigate the digital sphere safely.

Remember that, while Google makes the world’s knowledge available, it is up to us to consume and distribute it wisely.






